Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram
Profit is maximized by producing the quantity of output at which the marginal revenue of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost. Therefore if this firm chooses to produce sweaters it will produce 8000 sweaters per day the quantity at which marginal cost is equal to the price of 15 per sweater.
Principles Of Microeconomics Chapter 10 Monopoly
Rather they aim at the maximisation of profits in the long run.
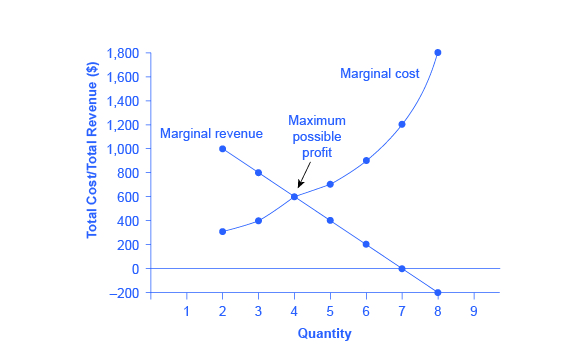
Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. At a price of 8 a profitmaximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market will produce 16000 pans per day as this is the quantity that corresponds to the point at which marginal cost equals the market price. So profit at the profit maximizing quantity is this green area right here price minus average cost times quantity. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram.
This is the end of the preview. Consequently the profit maximizing output would remain the same. This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
An increase in fixed cost would cause the total cost curve to shift up rigidly by the amount of the change. According to this principle price equals avcafc profit margin usually 10. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram consider a competitive market for shirts.
Sign up to access the rest of the document. There would be no effect on the total revenue curve or the shape of the total cost curve. So now we have a nice way of showing in a diagram exactly how much profit is.
Changes in total costs and profit maximization. On the previous graph use the blue rectangle circle symbols to shade the area representing the firms profit or loss if. For this they do not apply the marginalistic rule but they fix their prices on the average cost principle.
You know that economic profit is equal to total revenue tr minus total cost tc. Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. Sign up to view the full version.
The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. In the short run at a market price of 20 per candle this firm will choose to produce candles per day. Principle of marginal analysis the proposition that the optimal quantity is the quantity at which marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
Price dollars per shirt 6 12 18 output shirts 9000 18000 27000 total revenue dollars 54000 216000 486000 fixed cost dollars 81000 81000 81000 variable cost dollars profit dollars if a firm shuts down. Lets use this tool some more. Assume that the market for frying pans is a competitive market and the market price is 20 per frying pan.
Principle of average cost maximises profits. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram suppose that the market for candles is a competi. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram 3 profit.
Encyclonomic Web Pedia Monopoly Profit Maximization
 Suppose That The Market For Polo Shirts Is A Competitive Market The
Suppose That The Market For Polo Shirts Is A Competitive Market The
 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
 A Monopolist Faces A Demand Curve P 70 1q With Marginal Revenue
A Monopolist Faces A Demand Curve P 70 1q With Marginal Revenue
 Oligopoly Kinked Demand Curve Tutor2u Economics
Oligopoly Kinked Demand Curve Tutor2u Economics
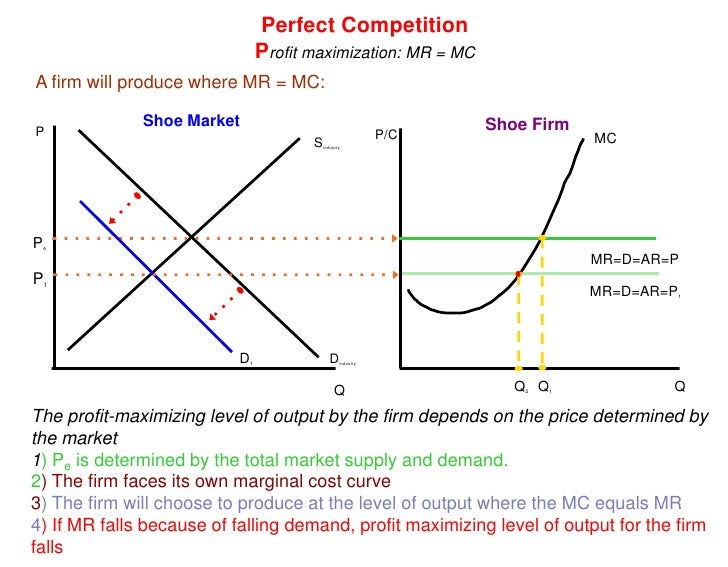 Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
 Gottheil Quiz Price And Output
Gottheil Quiz Price And Output
 Profit Maximization Problem By Figure Mc Marginal Cost Atc
Profit Maximization Problem By Figure Mc Marginal Cost Atc
Archive Fertiliser Manual Rb209 Appendix 11 Profit
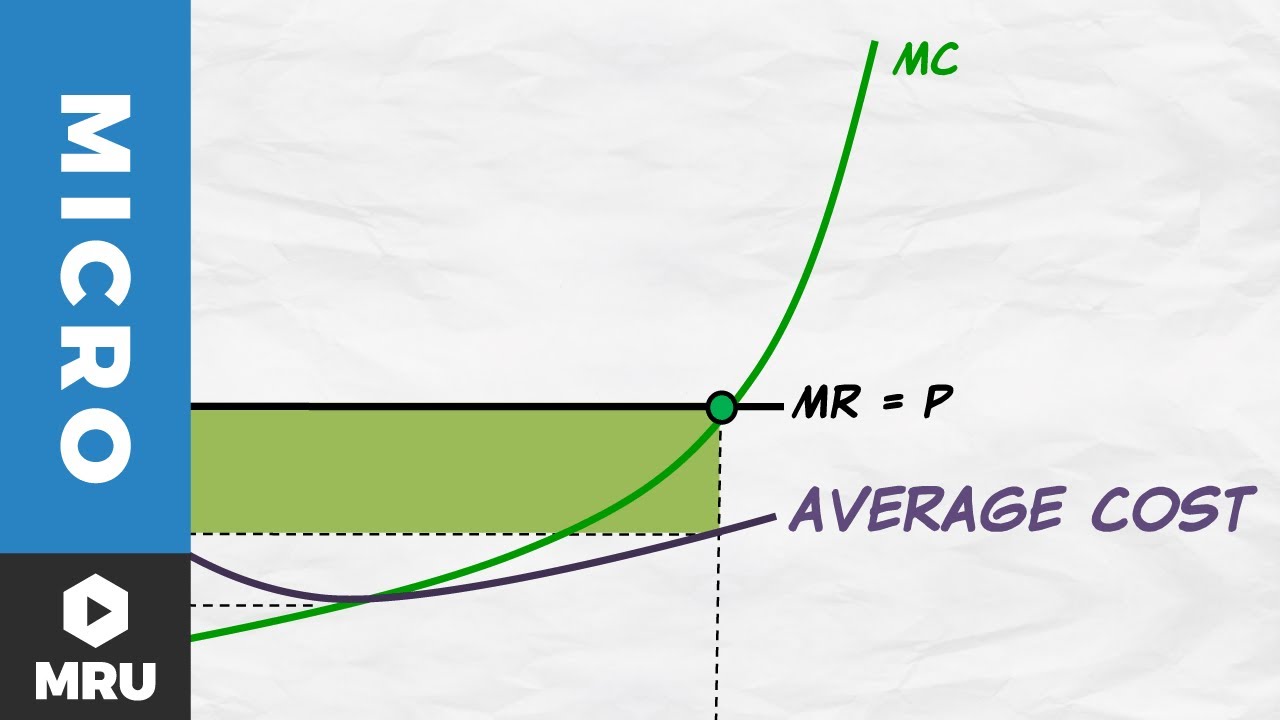 Maximizing Profit And The Average Cost Curve Youtube
Maximizing Profit And The Average Cost Curve Youtube
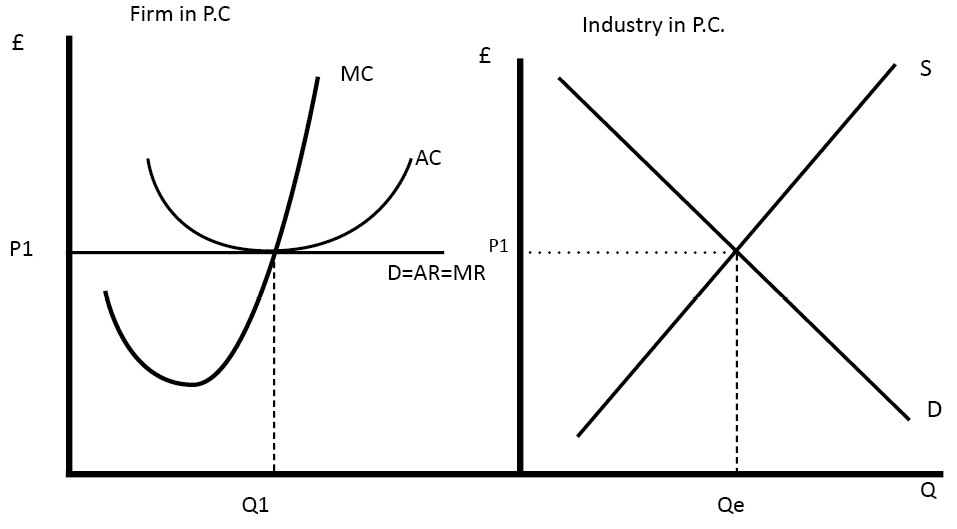 Profit Maximisation Economics Help
Profit Maximisation Economics Help
Profit Maximizing Monopolist Setting Single Price
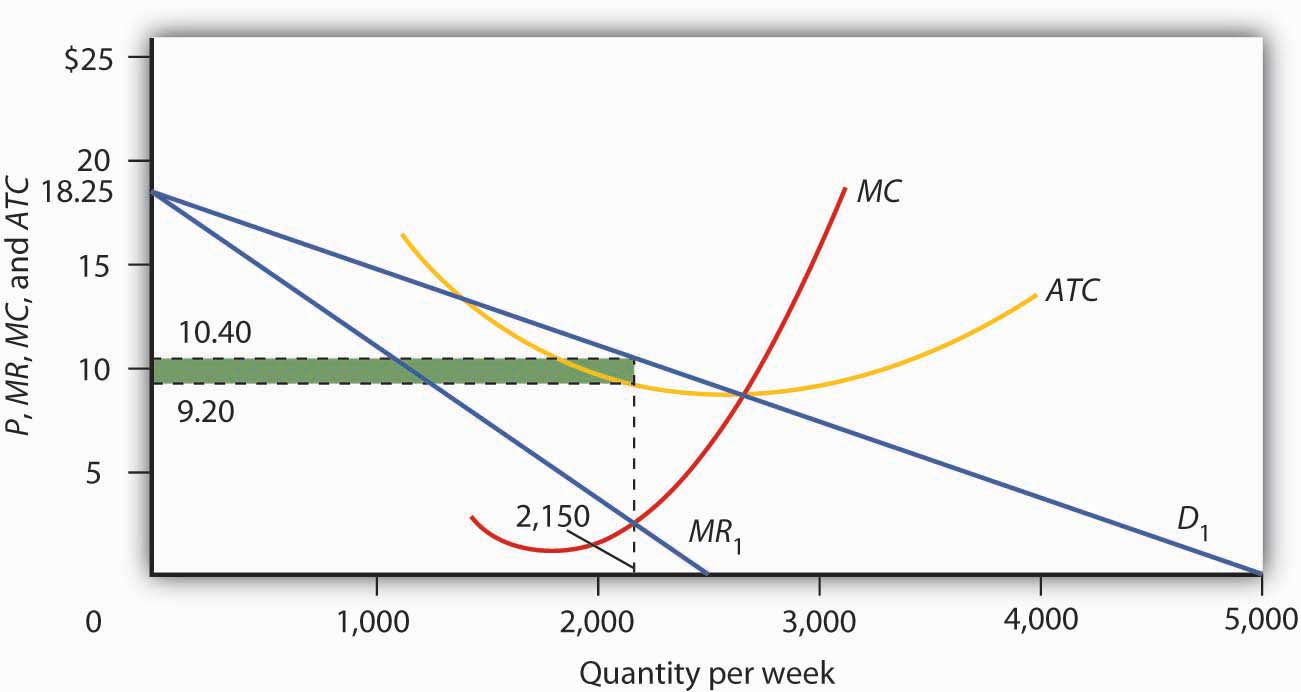 Discuss Profit Maximising Model In Detail College Paper Example
Discuss Profit Maximising Model In Detail College Paper Example
 Monopoly Profit Maximization With Quadratic Marginal Cost Wolfram
Monopoly Profit Maximization With Quadratic Marginal Cost Wolfram
Profit Maximization Model Of A Firm With Diagram
 Profit S Cool The Revision Website
Profit S Cool The Revision Website
Profit Maximization Cost Revenue And Profit

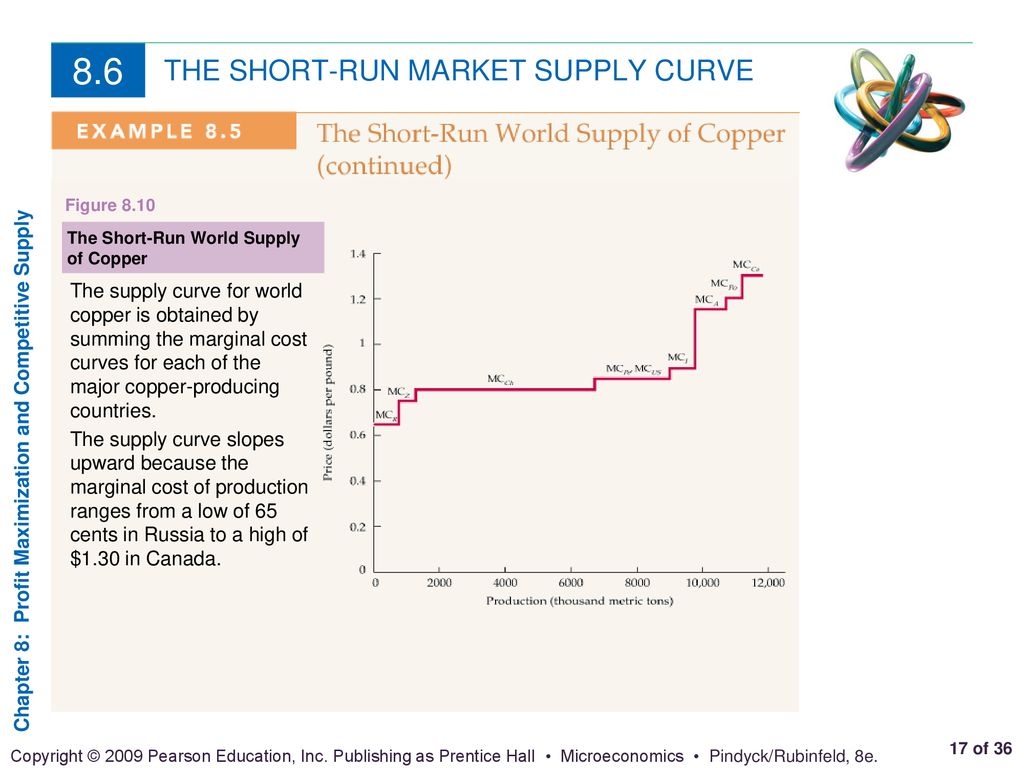 Chapter 8 Outline 8 1 Perfectly Competitive Markets 8 2 Profit
Chapter 8 Outline 8 1 Perfectly Competitive Markets 8 2 Profit
0 Response to "Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram"
Post a Comment