In An Diagram The Arrows Above The Attributes Indicate All Desirable Dependencies
In andiagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. In an diagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies.
Dependency if a table has multiple candidate keys and one of those candidate keys is a composite key the table can have based on this composite candidate key even when the primary key chosen is a single attribute.

In an diagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. The arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies ie dependencies that are based on the full primary key projnum empnum. A table where all attributes are dependent on the primary key and are independent of each other and no row contains two or more multivalued facts about an entity is said to be in. If a table has multiple candidate keys and one of those candidate keys is a composite key the table can have based on this composite candidate key even when the primary key chosen is a single attribute.
The arrows below the dependency diagram indicate less desirable dependencies partial dependencies not based on entire pk and transitive dependencies. The arrows above entities indicate all desirable dependencies in this table ie dependencies that are based on pk. This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
The default comparison condition for the subtype discriminator attribute is the comparison. The arrows above the attributes indicate all. Attribute a attribute b if all of the rows in the table that agree in value for attribute a also agree in value for attribute b.
Dependency c functionality d. The table is in 1nf as all arrows above the table in non key attributes indicate desirable relationships. Sign up to view the full version.
C1 and c3 are compound keys c2 has a partial dependency on c1 c4 and c5 have partial dependencies on c2 c5 depends on c4. A table that is in 1nf and includes no partial dependencies only is said to be in. The arrows below indicate the undesirable dependencies transitive and partial.
In an diagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. An exists when there are functional dependencies such that xy is functionally dependent on wz x is functionally dependent on w and xy is the primary key. Identify and discuss each of the indicated dependencies.
An is the attribute in the supertype entity that determines to which entity subtype each supertype occurrence is related.
Building Pi System Assets And Analytics With Pi Af
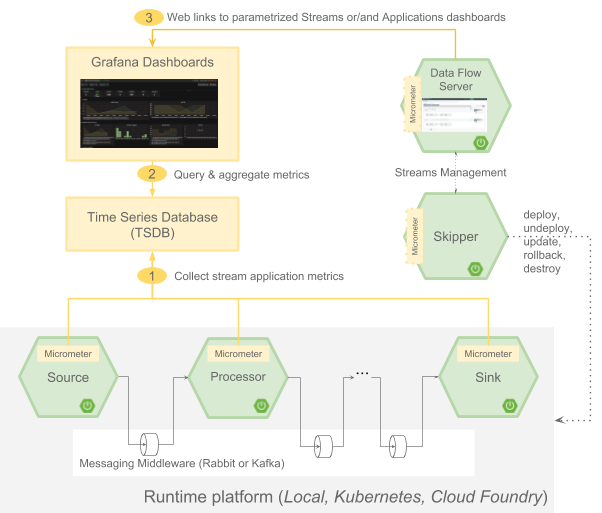 Spring Cloud Data Flow Reference Guide
Spring Cloud Data Flow Reference Guide
 Pdf Mechanisms Of Conscious And Unconscious Interpretative Processes
Pdf Mechanisms Of Conscious And Unconscious Interpretative Processes
 Pdf Systematic Reviews Of Research Postsecondary Transitions
Pdf Systematic Reviews Of Research Postsecondary Transitions

Chapter 6 Solutions Itc423 Database Systems Studocu
 Six Different Ways Part Ii Reflections On Psycholinguistic Theories
Six Different Ways Part Ii Reflections On Psycholinguistic Theories
 Evaluating Requirements Modeling Methods Based On User Perceptions
Evaluating Requirements Modeling Methods Based On User Perceptions
T E A C H Early Childhood Wisconsin Evaluation Report August 1999
 Selected Answer True Question 8 4 Out Of 4 Points In An Diagram The
Selected Answer True Question 8 4 Out Of 4 Points In An Diagram The
 True False Question 15 1 Normalization Represents A Micro View Of
True False Question 15 1 Normalization Represents A Micro View Of
 Ism3212 Quiz6 Docx 1 Dependency Diagrams Are Very Helpful In
Ism3212 Quiz6 Docx 1 Dependency Diagrams Are Very Helpful In
Biopython Tutorial And Cookbook
Chapter 6 Solutions Itc423 Database Systems Studocu
 A Table That Is In 2nf And Contains No Transitive Dependencies Is
A Table That Is In 2nf And Contains No Transitive Dependencies Is
Jelber Sayyad Shirabad Phd Thesis Supporting Software Maintenance
 True False Question 15 1 Normalization Represents A Micro View Of
True False Question 15 1 Normalization Represents A Micro View Of
Chapter 6 Solutions Itc423 Database Systems Studocu
 Pdf Software Architecture Built From Behavior Models
Pdf Software Architecture Built From Behavior Models
Biopython Tutorial And Cookbook

0 Response to "In An Diagram The Arrows Above The Attributes Indicate All Desirable Dependencies"
Post a Comment