Use The Diagram To Determine What Flower Structures Develop Under The Conditions Described Below
Below is an image of a wild type arabidopsis thaliana flower and a diagram of the flower outlining the four whorls. A small dish or container filled with talcum powder.
 Plant Reproductive System Britannica Com
Plant Reproductive System Britannica Com
Abc genes and the development of floral structures this diagram shows how gene activity in wild t.

Use the diagram to determine what flower structures develop under the conditions described below. Develop where only a genes are active. Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. Most animal cells however contain the structures shown in the diagram.
In this activity you will explore how homeotic genes control the development of the flower structures. Ask them to identify and write down each plant part described below. Develop where a and b genes are active.
Develop where b and c genes are active. Develop where only c genes are active. The abc model of flowering as an arabidopsis flower develops the floral meristem produces four floral structures in concentric circles or whorls.
Which reproductive process determines the traits present in the cluster of cells. Wild type arabidopsis flowers have from outside to inside 4 sepals which are not clearly visible in the photograph 4 petals 6 stamens and 2 carpels which fuse to form the central pistil. In the chart below identify the structures that will develop in each whorl in the mutant flowers.
13the diagram below represents a technique used to produce carrots. Use the diagram to determine what flower structures develop under the conditions described below. The structures in wild type flowers and one mutant have already been filled in for you drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the chart.
Develop where a and b genes are active. Use the diagram to determine what flower structures develop under the conditions described below develop where only a genes are active. Below is a generic plant cell diagram.
Label structures and processes using white labels indicate whether different structures are haploid or diploid using pink labels and indicate the types of cell division that occur at different points in the life cycle using blue labels. Develop where b and c genes are active. Labels can be used once more than once or not at all.
Nerve cells bone cells and liver cells for example all develop in ways that enable them to better perform their specific duties. Give each student a photocopy of flower diagram. 14base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents stages in the digestion of a starch and on your knowledge of biology.
The structure of plant cells can vary during the early stages of growth. Hydrogen bonds are broken when water molecules. Have them study the line drawing of the flower.
The diagram below illustrates the alternation of generations that is characteristic of the angiosperm life cycle. You can also use corn starchflour or different colors of chalk dust.
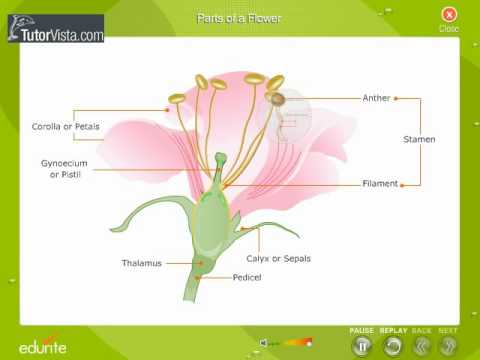
The Structure And Functions Of Flowers
 Pollination Ecology Britannica Com
Pollination Ecology Britannica Com
The Structure And Functions Of Flowers
 Angiosperm Reproductive Structures Britannica Com
Angiosperm Reproductive Structures Britannica Com
 B8 2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Accelerated Study Notes
B8 2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Accelerated Study Notes
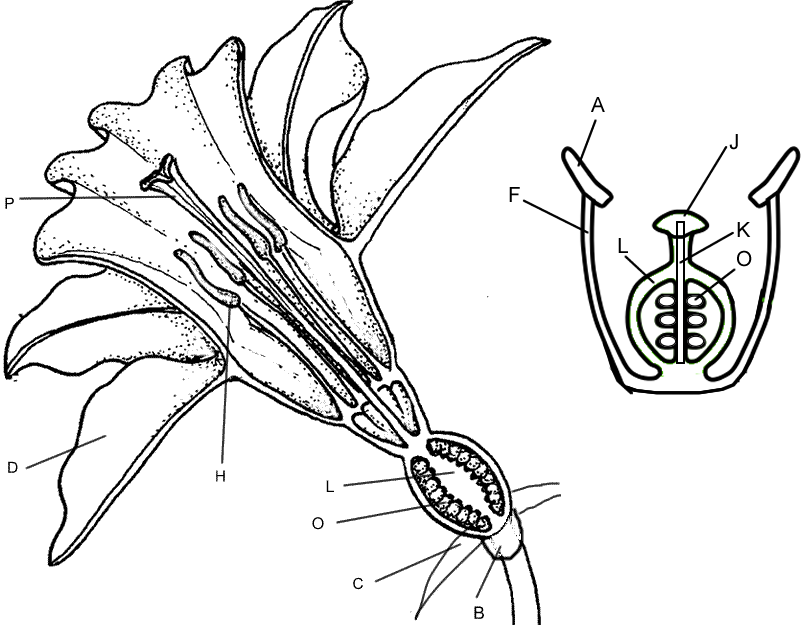 Flower Structure And Reproduction
Flower Structure And Reproduction
Pollination And Fertilization Boundless Biology
 Angiosperm Description Evolution Characteristics Taxonomy
Angiosperm Description Evolution Characteristics Taxonomy
The Structure And Functions Of Flowers
Plant Reproduction Biology 1520
 How Do Plants Deal With Dry Days Frontiers For Young Minds
How Do Plants Deal With Dry Days Frontiers For Young Minds



0 Response to "Use The Diagram To Determine What Flower Structures Develop Under The Conditions Described Below"
Post a Comment