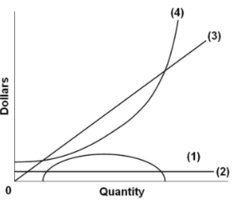
Curve 2 In The Diagram Is A Purely Competitive Firms
A total cost curve. Key points for pure competition in the long run.
 8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 45.

Curve 2 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms. This means the firm is. Total economic profit curve. For a purely competitive firm.
Assume for a competitive firm that mc avc at 12 mc atc at 20 and mc mr at 16. Curve 4 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. Total economic profit curve.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 45. Curve 2 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms. C marginal revenue curve b total revenue curve.
This is the end of the preview. A standardized or homogeneous product d. No barriers to the entry or exodus of firms c.
A firm is producing an output such that the benefit from one more unit is more than the cost of producing that additional unit. See table for tr mr a the industry is purely competitivethis firm is a price taker the firm is so small relative to the size of. Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 46.
Producing less output than allocative efficiency requires. Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. Curve 4 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms.
In answering the question assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axisrefer to the information. Marginal revenue will graph as an upsloping line. Economic surplus is maximized in pure competition.
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 46. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn positive economic profits in the long run. Ease of entry will cause long run economic profits to be zero.
In the long run purely competitive firms will be both productive and allocatively efficient. Atotal cost curvegif b. A purely competitive seller should produce rather than shut down in the short run.
Short run economic profits losses leads to firms entering exit the industry. D total economic profit curve. Considerable nonprice competition b.
Curve 1 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. Realize a profit of 4 per unit of output. Curve 2 horizontal line in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms.
The demand curve will lie above the marginal revenue curve. A large number of buyers and sellers 2. Curve 3 in the diagram above is a purely competitive firms.
The market that it can change its level of output without affecting the market price.
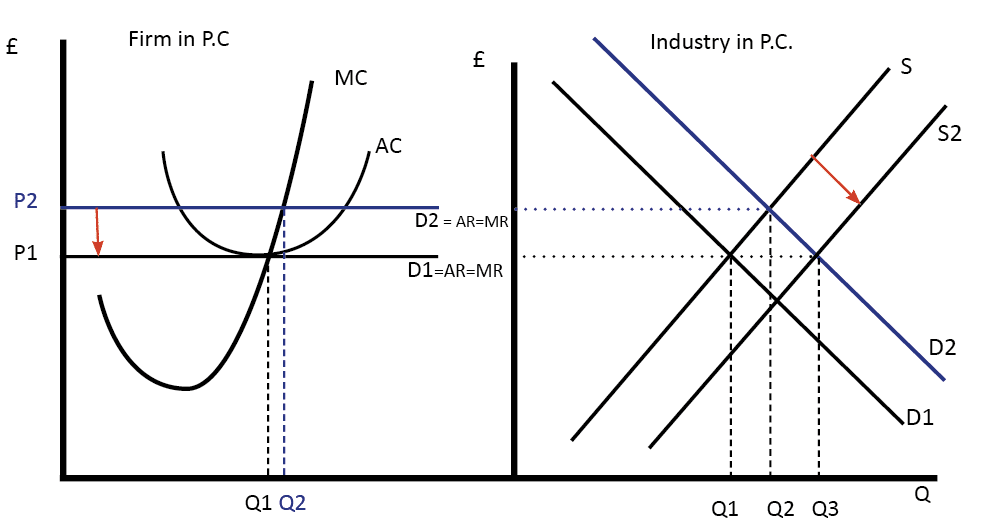 Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help
Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help
 Solved 3 Quantity Curve 4 In The Diagram Is A Purely C
Solved 3 Quantity Curve 4 In The Diagram Is A Purely C
![]() Perfect Competition I Long Run Supply Curve Policonomics
Perfect Competition I Long Run Supply Curve Policonomics
Economic Efficiency In Perfect Competition And Monopoly
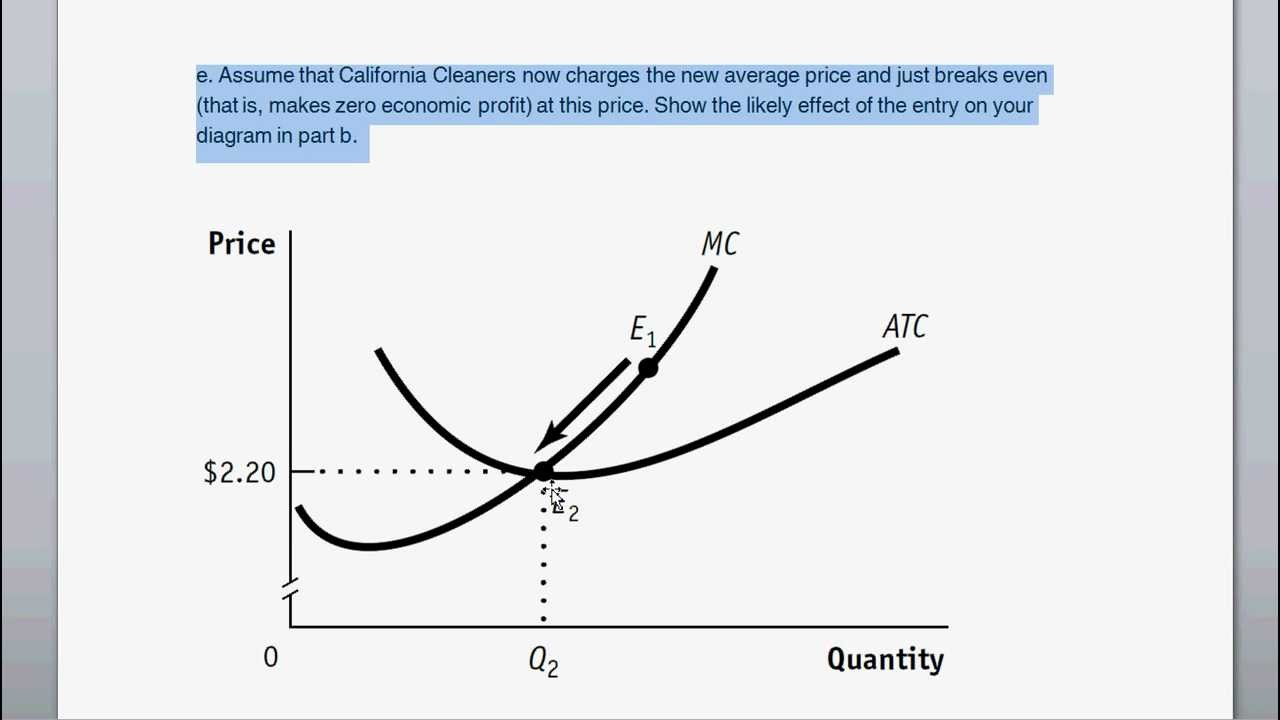 Example Of A Firm In A Perfectly Competitive Market Economic
Example Of A Firm In A Perfectly Competitive Market Economic
Curve 2 In The Diagram Is A Purely Competitive Firm S Manicpixi
Equilibrium Of The Firm In The Short Run With Diagram
Monopoly V Perfect Competition

 Perfect Competition Boundless Economics
Perfect Competition Boundless Economics
Short Run Supply Curve Of A Competitive Firm And Industry With Diagram
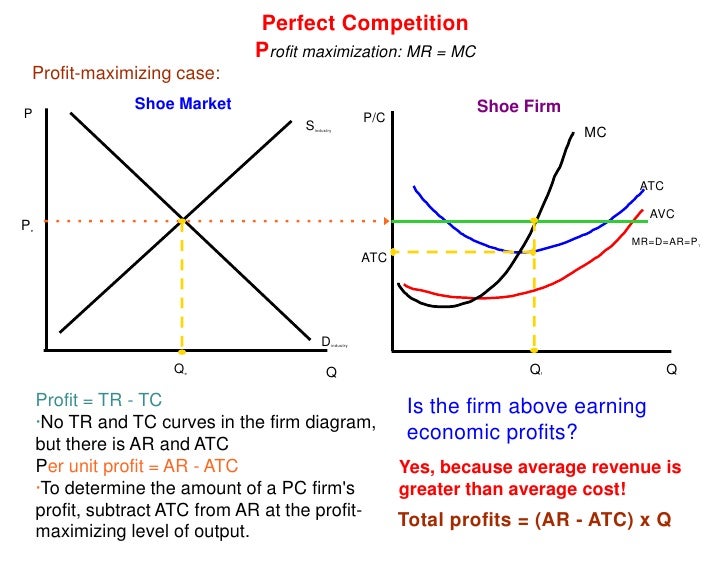 Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
Economics Exam Questions Economics Exam Answers
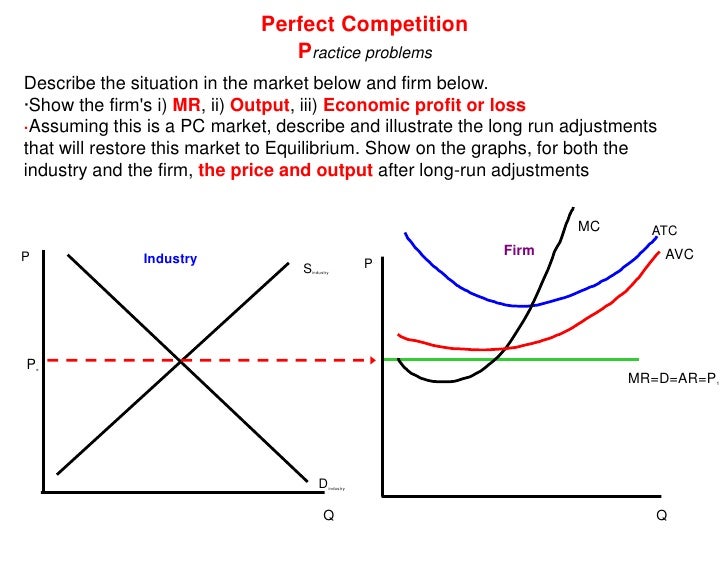 Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition
 Refer To The Above Diagram Which Pertains To A Purely Competitive
Refer To The Above Diagram Which Pertains To A Purely Competitive
 Econ160 Practice Questions Chapters 7 9 10 11 Free Essays
Econ160 Practice Questions Chapters 7 9 10 11 Free Essays

0 Response to "Curve 2 In The Diagram Is A Purely Competitive Firms"
Post a Comment