Buoyant Force Free Body Diagram
Archimedes principle and buoyant force. Buoyant force example problems.
The ball has a mass of 05 kg and a diameter of 22 cm.
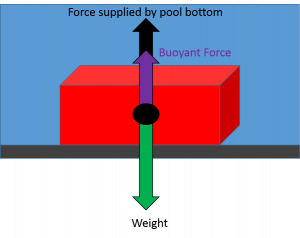
Buoyant force free body diagram. A basketball floats in a bathtub of water. Ing the buoyant force must be greater than or equal to the weight of the object. In physics and engineering a free body diagram force diagram or fbd is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces movements and resulting reactions on a body in a given condition.
In this case the raft and the chests are in a fluid and the force due to the pressure of a fluid is called the buoyant force. Buoyant force example problems. This huge oil tanker stays afloat because it displaces more than its own weight in water.
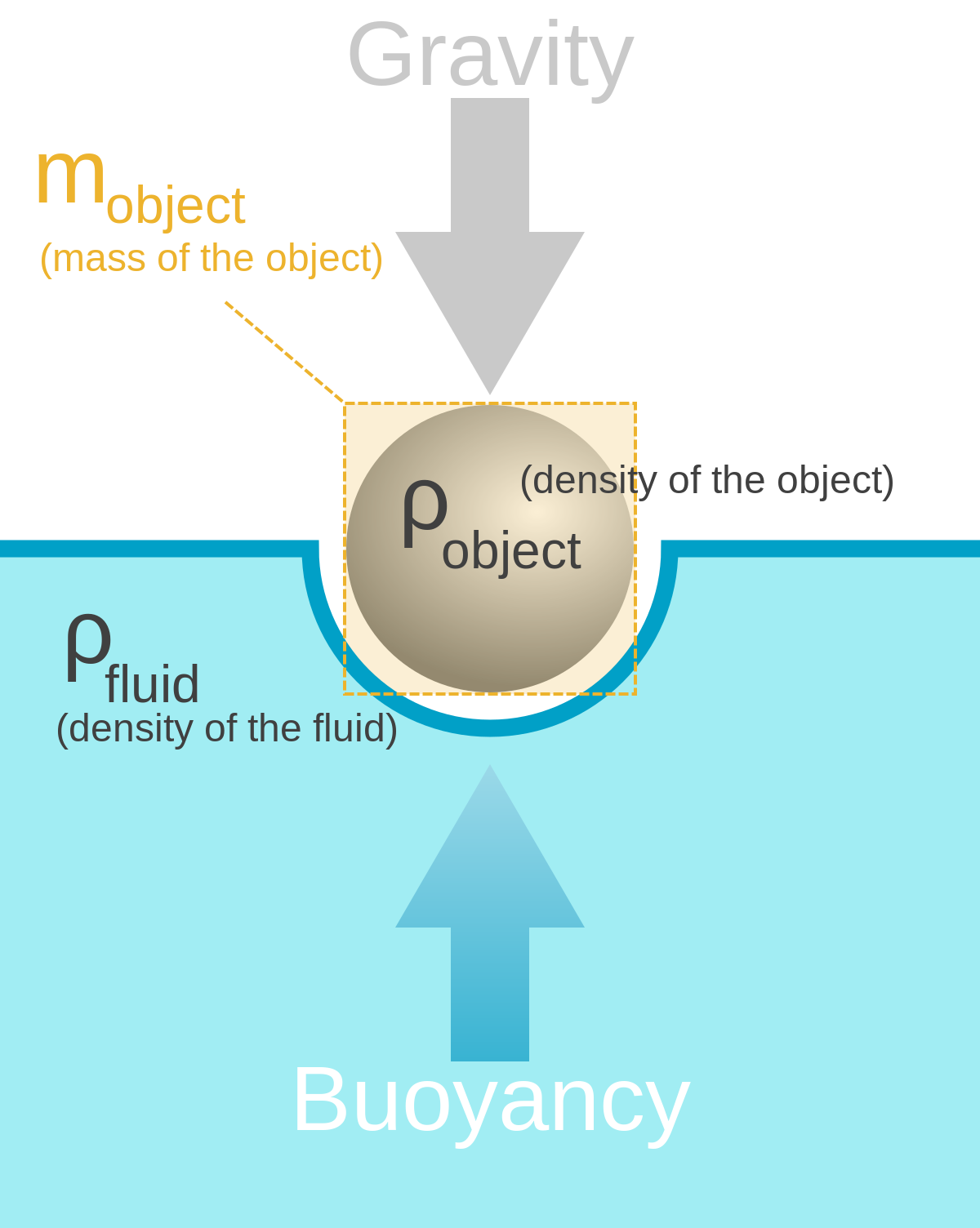
Gravity buoyancy the force applied by the engine and friction with the water. Archimedes principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid whether fully or partially submerged is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces and acts in the upward direction at the center of mass of the displaced fluid wikipedia emphasis mine. Mobject mfluid displaced figure 3.
B what is the volume of water displaced by the ball. Density buoyancy and free body diagrams updated. 7 jan 16 page 1 of 4 deviill pphyyssiiccss ba ddeesstt lcclaassss poonn caammpuuss density buoyancy and force diagrams this lab was adapted from a lab submitted to phet by chris bires of spring valley hs on 10132010 and.
Normal force is the contact force between two surfaces. It discusses how to use free body diagrams to calculate the tension. The key to many buoyancy problems is to treat the buoyant force like all the other forces weve dealt with so far.
They depict a body or connected bodies with all the applied forces and moments and reactions which act on the bodyies. It pushes out from the surfaces and keeps them from falling into each other. A what is the buoyant force.
Archimedes principle and buoyant force. Why isnt normal force included on the free body diagram. Upward buoyant force to each block.
Whats the first step. What is buoyant force. A diagram of the blocks we will place in a beaker of water and the free body diagram.
Draw a free body diagram. There are four forces acting on the boat in this example. This is the currently selected item.
Thus the free body diagram for a boat looks. Using this diagram determine the magnitude of the frictional force caused by the water against the boat and the magnitude of the buoyant force. Buoyant force and archimedes principle.
It explains how to calculate the upward buoyant force acting on an object and it shows how to derive the buoyant force formula. The free body diagram of a float ing object shows equal and opposite forc es of buoyancy and weight. Compare the free body diagrams in figure 91 when the blocks are in equilibrium on the table with the free body diagrams in figure 94 when the blocka chapter 9 fluids page 9 2 figure 91.
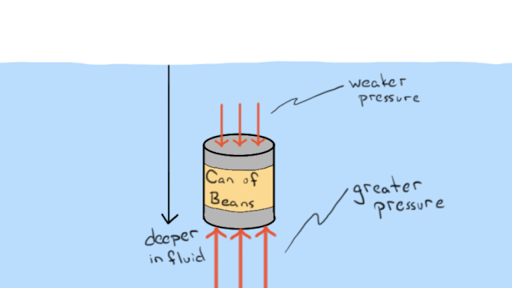
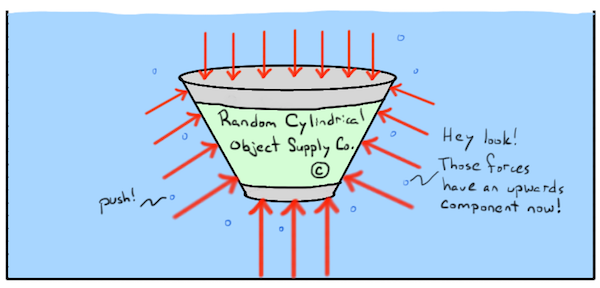 What Is Buoyant Force Article Fluids Khan Academy
What Is Buoyant Force Article Fluids Khan Academy
 Human Movement In A Fluid Medium Basic Biomechanics 7e
Human Movement In A Fluid Medium Basic Biomechanics 7e
 Newton S Third Law On A Scale Balance Iopscience
Newton S Third Law On A Scale Balance Iopscience
Lab 8 Buoyancy And Archimedes Principle
 Does The Buoyancy Force Work On An Object Which Is Not Fully
Does The Buoyancy Force Work On An Object Which Is Not Fully
 Classical Mechanics Floating Objects And Weight Physics Stack
Classical Mechanics Floating Objects And Weight Physics Stack
 Archimedes Principle Buoyant Force Acting On Stock Vector Royalty
Archimedes Principle Buoyant Force Acting On Stock Vector Royalty
 Buoyancy Force Diagram 10 Ulrich Temme De
Buoyancy Force Diagram 10 Ulrich Temme De
 The Scale At The Bottom Of A Pool Wired
The Scale At The Bottom Of A Pool Wired
 Physics 111 Fundamental Physics I Physics Of Cooking Corn
Physics 111 Fundamental Physics I Physics Of Cooking Corn
Marine Mammals The Physics Of Aquatic Life
 The Scale At The Bottom Of A Pool Wired
The Scale At The Bottom Of A Pool Wired
 Under Water Weight Body Physics Motion To Metabolism
Under Water Weight Body Physics Motion To Metabolism
 Center Of Buoyancy Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript
Center Of Buoyancy Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript
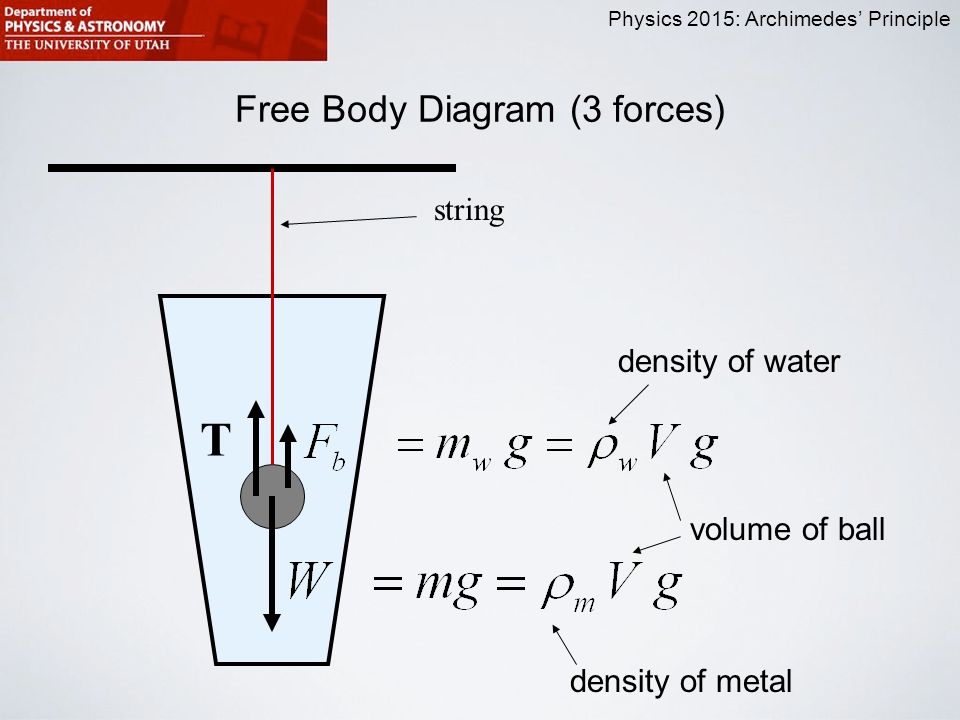 Purpose The Purpose Of Today S Lab Is To Investigate Archimedes
Purpose The Purpose Of Today S Lab Is To Investigate Archimedes
 Free Body Diagram Highlighting The Three Primary Forces Exerted On A
Free Body Diagram Highlighting The Three Primary Forces Exerted On A
0 Response to "Buoyant Force Free Body Diagram"
Post a Comment