If The Competitive Firm Depicted In This Diagram Produces Output Q It Will
Refer to the above diagram. Firms tot leave the industry market supply to fall and product price to rise.

The diagrams portray both long run and short run equilibrium.
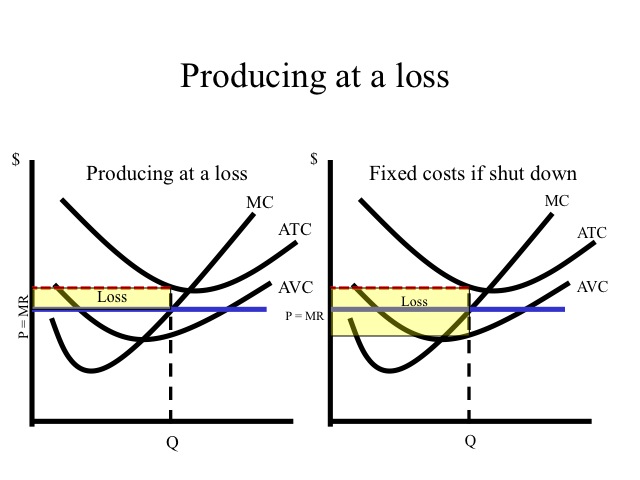
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will. The diagrams portray long run equilibrium but not short run equilibrium. Pmrar only true in perfectly competitive market 2 condition for profit maximization is mrmc true in any type of market 3 combine these two results together. For a profit maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive.
Earn a normal profit. 100 point if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will suffer an economic loss. D what is the firms total profit or loss at the profit maximizing or loss minimizing quantity.
In industries with high fixed costs it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms. Earn a normal profit. Suffer an economic loss.
Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Market it will choose the output where price is equal to marginal cost. Earn an economic profit.
Refer to the above diagram. C the firms goal is to charge a high price and make a small profit rather than a low price and no profit. Demand is relatively elastic.
C what is the total cost to produce the profit maximizing or loss minimizing quantity. Achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. Earn an economic profit.
E the monopolistically competitive firm depicted in the diagram is. This preview has intentionally blurred sections. In the long run we should expect.
If this competitive firm produces output q it will. Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. If a firm is in a competitive market and produces at q2 its average costs will be ac2.
Suffer an economic loss. Of unimpeded entry to the industry. Sign up to view the full version.
Refer to the above diagram. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will a. A monopoly can increase output to q1 and benefit from lower long run average costs ac1.
Earn a normal profit. Suppose losses cause industry x to contract and as a result the prices of relevant inputs decline. Earn an economic profit.
Achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. The diagrams portray short run equilibrium but not long run equilibrium. A purely competitive firm is precluded from making economic profits in the long run because.
B although its average cost of production is lower when the firm produces q g units to be able to sell its output the firm will have to charge a price below average cost resulting in a loss. Refer to the diagram. If this competitive firm produces output q it will.
Achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. B what price will the firm charge to sell the output indicated in question a.
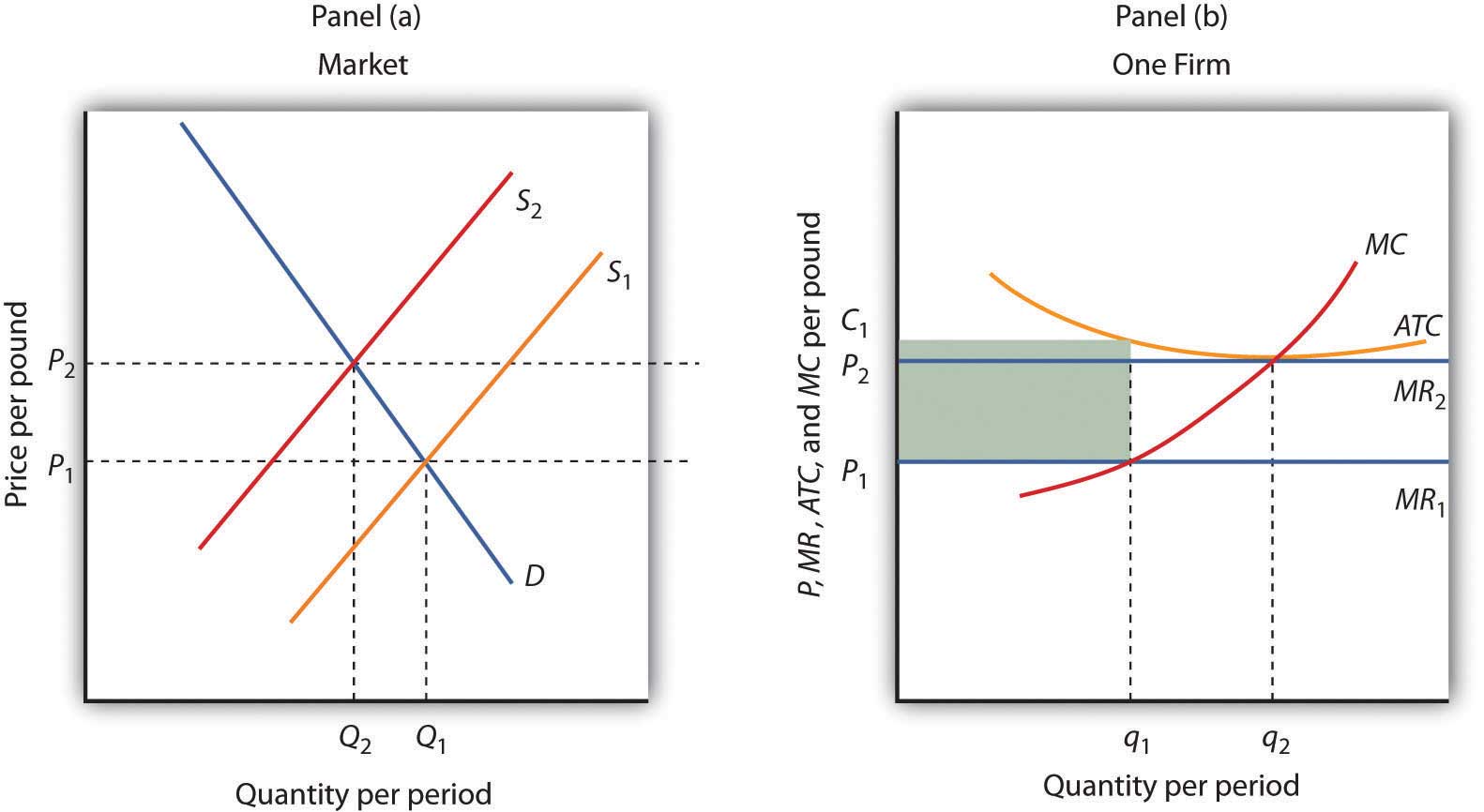 Perfect Competition In The Long Run
Perfect Competition In The Long Run

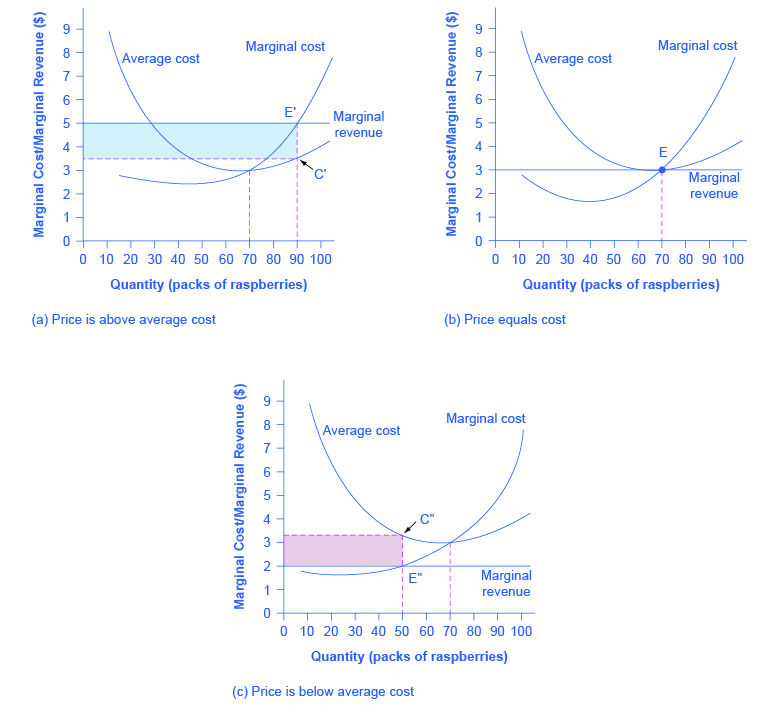 Reading Profits And Losses With The Average Cost Curve Microeconomics
Reading Profits And Losses With The Average Cost Curve Microeconomics
 The Economy Unit 7 The Firm And Its Customers
The Economy Unit 7 The Firm And Its Customers
Pricing In Theory With Diagram
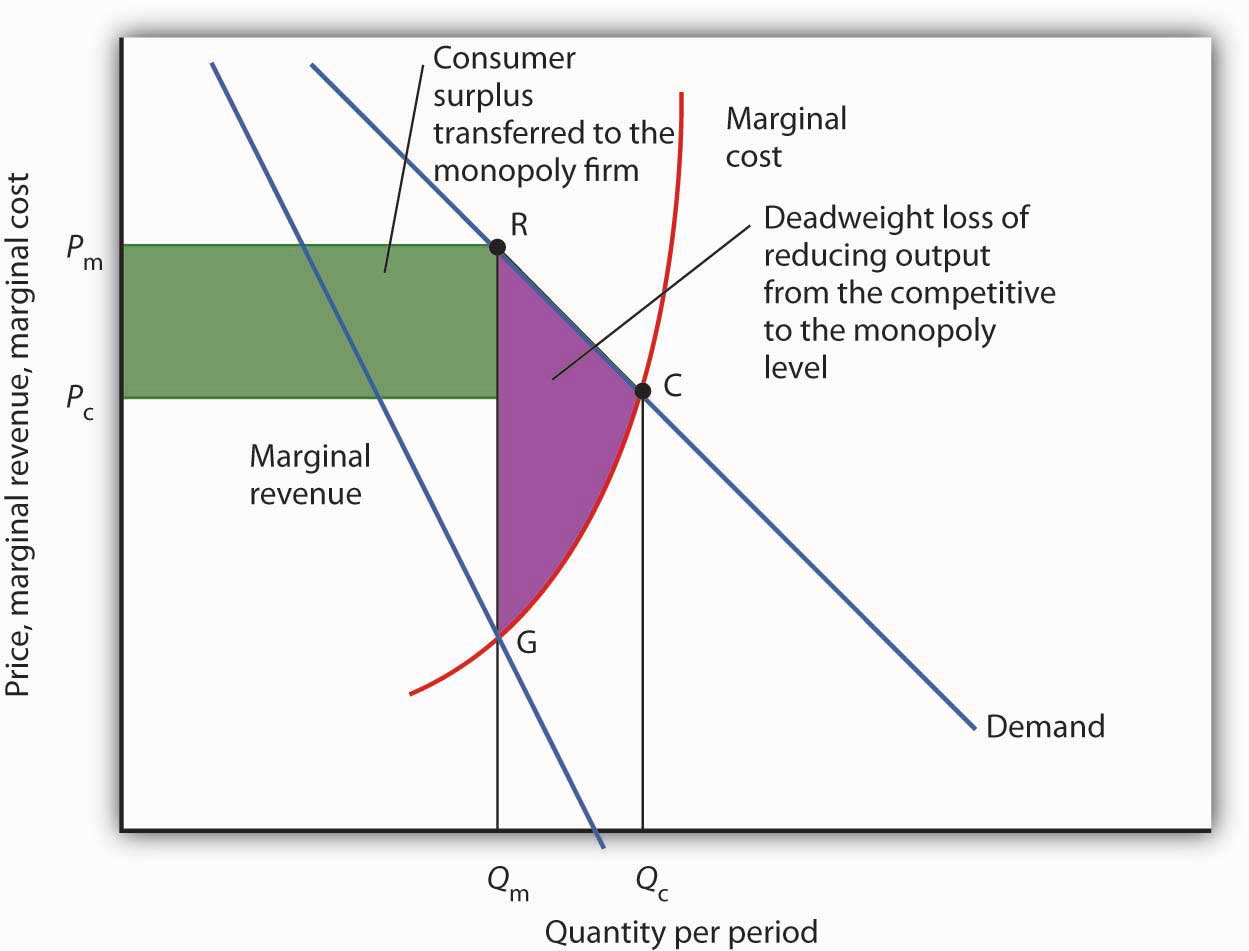
 The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
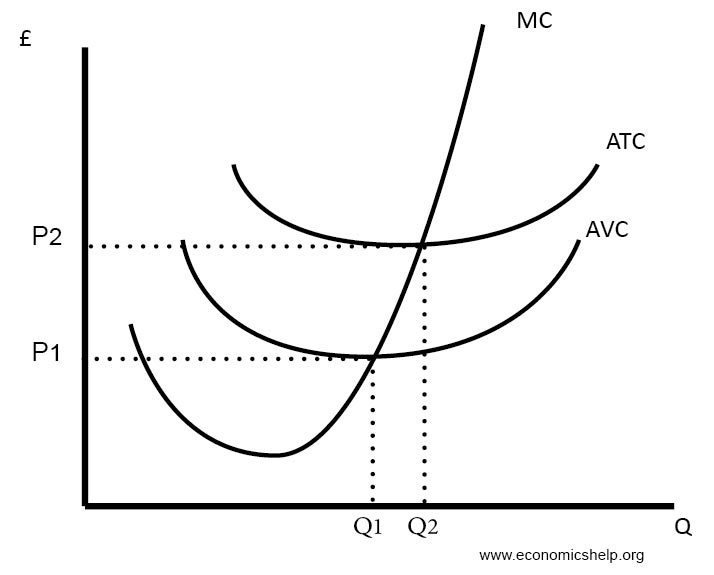 Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
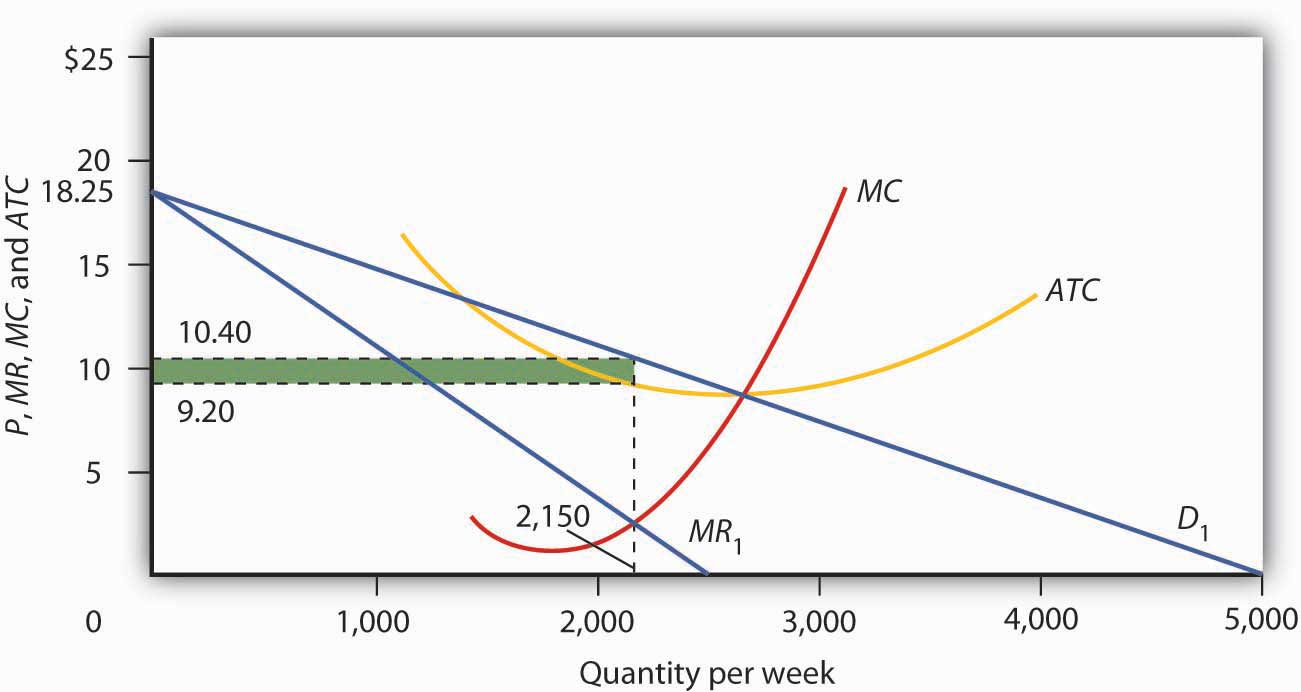 Monopolistic Competition Competition Among Many
Monopolistic Competition Competition Among Many
 7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
 The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
13monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly
 7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
 The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
The Economy Unit 8 Supply And Demand Price Taking And Competitive
Supply Curve Of A Firm And Industry With Diagram
0 Response to "If The Competitive Firm Depicted In This Diagram Produces Output Q It Will"
Post a Comment