Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Far From The Lens
A ray parallel to the principal axis that passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens.
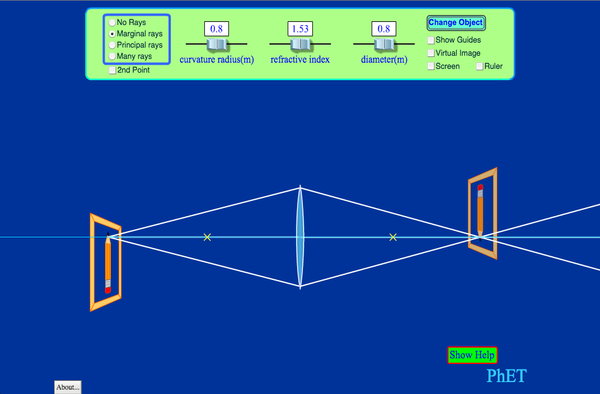 Geometric Optics Refraction Lens Optics Phet Interactive
Geometric Optics Refraction Lens Optics Phet Interactive
For an object that is further away from the lens than 2f.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens. Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. Start by drawing the ray parallel to the optical axis from the object incident onto the lens and refracted through the focus. A rays through the center of the lens that does not change direction.
The first picture below shows how to draw a ray diagram. B use a ruler to measure the object distances image distances and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the middle of the lens.
In the three cases described above the case of the object being located beyond 2f the case of the object being located at 2f and the case of the object being located between 2f and f light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. Parallel to the principal axis of the lens. For aconvex lens we draw the ray diagram as follows.
The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. It is sort of the inverse. If an object is located between the focal point and converging lens the image will be.
The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Extend both rays as much as you can line in blue. Its direction is not changed.
It is refracted by the lens to pass through the focal point. Then from the optical axis on the image side. Further down the page there is a picture showing.
Ray diagrams for images made by a convex lens. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. Ray diagram for object located in front of the focal point.
Through the focal point in front of the lens. The type of image made by a convex lens. From the tip of the object arrow.
Introduction refraction and lenses 5. Step by step method for drawing ray diagrams. Depends on how far away the object is.
Ray diagrams for lenses. Through the center of the lens. 2 give me a thumbs up for this video.
Support my channel by doing all of the following. A ray diagram for an object that is between f and 2f. 1 subscribe get all my excellent physics chemistry and math videos.
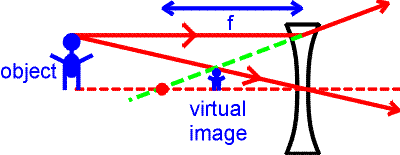
Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore the image will be upright reduced in size smaller than the object and virtual.
A ray through the focal point in front of the lens that emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens.
The Reflection And Refraction Of Light
 Drawing Ray Diagrams For Plane Mirrors Mini Physics Learn
Drawing Ray Diagrams For Plane Mirrors Mini Physics Learn
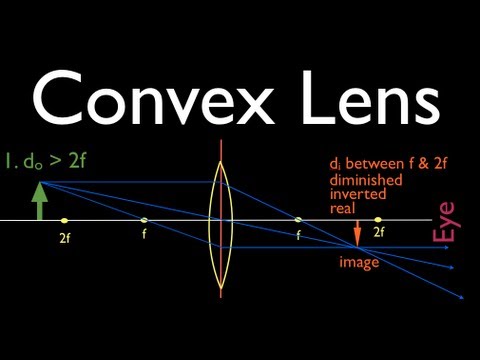 Ray Diagrams 2 Of 4 Convex Lens Youtube
Ray Diagrams 2 Of 4 Convex Lens Youtube
Where The Image Will Be Formed In A Concave Mirror If The Object Is
From Lenses To Optical Instruments
 Light Reflection And Refraction S Chand Dronstudy Com
Light Reflection And Refraction S Chand Dronstudy Com
Image Formation By Thin Lenses
 Image Formation In Convex Lenses A When An Object Is Placed In
Image Formation In Convex Lenses A When An Object Is Placed In
Ask Questions For Cbse Class 10 Physics Light Reflection Refraction
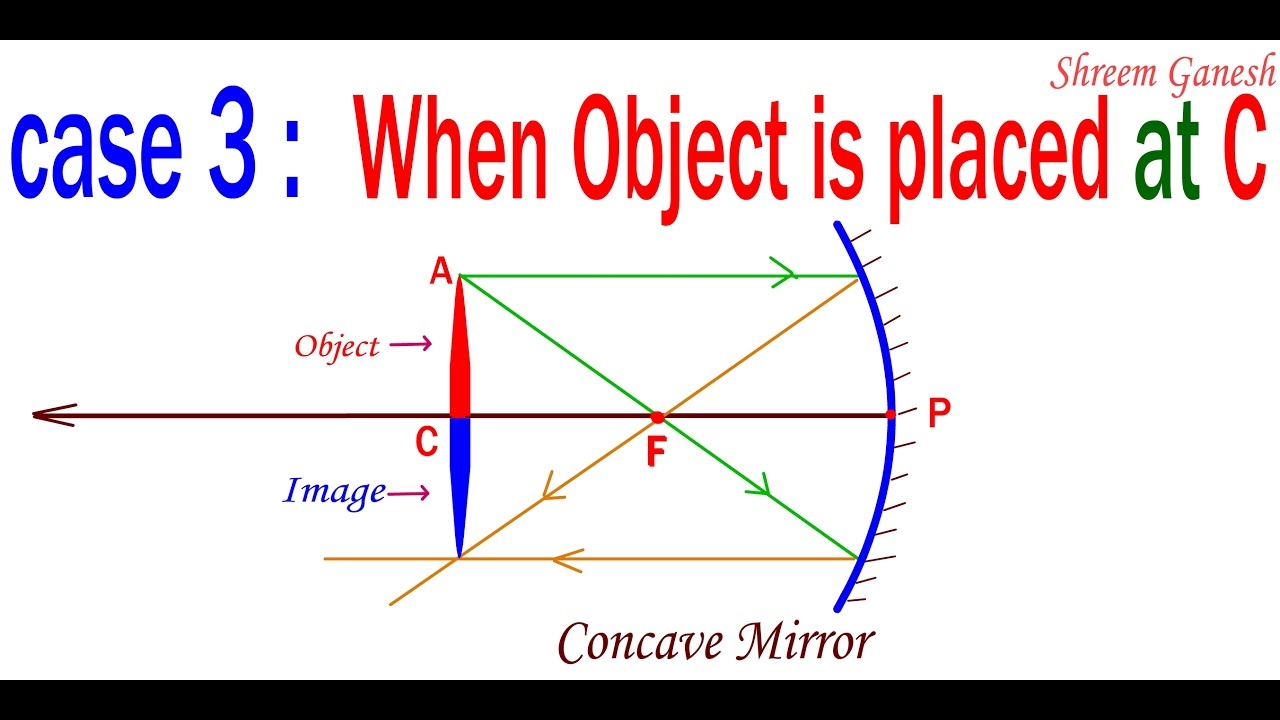 When Object Is Placed At C Centre Of Curvature Of A Concave Mirror
When Object Is Placed At C Centre Of Curvature Of A Concave Mirror
Image Formation By Lenses Physics
 Concave Lens Concave Lens Ray Diagram Physics Tutorvista Com
Concave Lens Concave Lens Ray Diagram Physics Tutorvista Com
Lenses And Optical Instruments
 Homework And Exercises How To Draw A Ray Diagram From Focal Length
Homework And Exercises How To Draw A Ray Diagram From Focal Length
 Icse Solutions For Class 10 Physics Refraction Of Light A Plus
Icse Solutions For Class 10 Physics Refraction Of Light A Plus
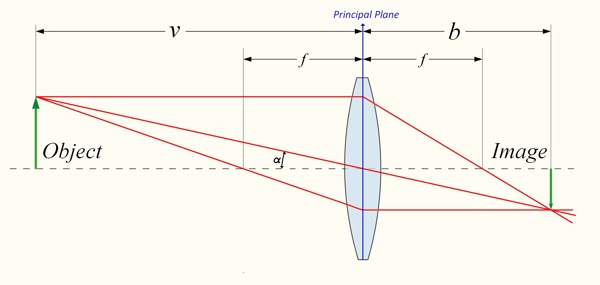 How To Use The Thin Lens Formula To Model A Thick Lens Panohelp Com
How To Use The Thin Lens Formula To Model A Thick Lens Panohelp Com
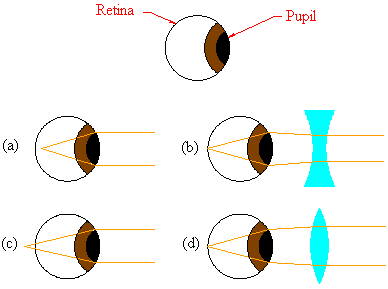 Applications Of Mirrors And Lenses
Applications Of Mirrors And Lenses

0 Response to "Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Far From The Lens"
Post a Comment